Driving edge missions with commercial innovation
By Chris Christou, Jennifer Congdon, and Andrew Bolka
At a forward operating base in contested territory, enemy surveillance units are advancing toward a military communications hub. In conventional 5G deployments, this scenario presents decision makers with a difficult choice: maintain current radio emission control (EMCON) levels and risk detection by the adversary’s electronic warfare systems or shut down communications and lose situational awareness. But this network operates differently.
Within seconds of threat detection, machine learning (ML) algorithms running on the installation’s private 5G infrastructure begin autonomously reconfiguring transmission parameters. The unit’s network monitors the tactical environment and automatically adjusts power levels across base stations. The network’s coverage area contracts and reshapes itself, maintaining some connectivity while reducing its electromagnetic signature enough to evade enemy sensors.
This scenario illustrates the emerging reality of artificial intelligence-radio access networks (AI-RAN), a technological breakthrough that transforms wireless networks from passive data pipes into intelligent, adaptive platforms. This evolution represents the technical foundation for future networks to unlock innovative new edge applications and devices.
Speed Read
AI-RAN transforms wireless networks from passive data pipes into intelligent, adaptive platforms, optimizing network performance and enabling edge applications using the same infrastructure.
AI-RAN is the foundation for the future 6G stack, with its technical development offering the United States an opportunity to reclaim leadership in the global telecom arena by leveraging a wealth of differentiating software and AI expertise.
Current 5G-Advanced infrastructure supports AI-RAN, allowing agencies to begin benefiting from the technology today while developing readiness for the upcoming 6G era.
What makes AI-RAN so powerful is its ability to solve two strategic challenges with the same technology. Specifically, AI for RAN optimizes network performance by automatically adjusting settings that normally require manual intervention, allowing base stations to detect problems and fix themselves without central control. AI on RAN enables AI applications to run directly on the same equipment as the RAN itself instead of on remote servers, reducing delays and enabling new capabilities in austere environments.
As the telecom industry maps sweeping transformations in the coming years, AI-RAN will also become the foundation of the future 6G stack. This means the geopolitical stakes for the development of these advanced networking capabilities could not be higher. 6G has become a key technology for national security and economic competitiveness, with the United States and its allies committing to “support open, free, global, interoperable, reliable, resilient, and secure connectivity” as a means to promote stability and peace.
While previous wireless generations were mostly static, 6G networks will be software- and AI-based and easier to rapidly reconfigure. The AI-RAN platform’s architectural flexibility will enable nations with advantages in software and AI expertise to better access the innovation this critical infrastructure promises to unlock. Consequently, AI-RAN offers a strategic opportunity for the United States to reclaim leadership in the global telecom arena. By moving quickly and leveraging the disaggregated, software-defined nature of AI-RAN architectures, America can play a pivotal role in building the AI-native wireless standards and technologies that will define connectivity’s next generation and compete more effectively in the global marketplace.
America’s AI-RAN Opportunity
China has significant mobile network market share globally, from 5G infrastructure to handset manufacturing. This position extends beyond deployment to standard setting, pricing leverage, and geopolitical influence over spectrum policy and infrastructure exports.
China’s centralized decision making has enabled rapid scaling and aggressive global expansion of its telecom model. For America, ceding leadership in wireless communications erodes both economic competitiveness and the resilience of critical communications infrastructure. Spectrum represents a finite national asset. Whoever wields it most efficiently gains outsized geopolitical and commercial leverage.

AI-RAN presents a unique opportunity for America to reverse this dynamic. By combining U.S. strengths in advanced semiconductors, cloud infrastructure, and AI innovation, the nation can leapfrog static approaches and pioneer intelligent, adaptive allocation. AI-RAN transforms wireless networks from a constrained, zero-sum resource into a dynamic, software-defined asset, enabling networks that are faster, more efficient, and more resilient than centralized alternatives.
This approach allows America to reassert control over spectrum optimization, set the pace for global standards, and demonstrate innovation-driven leadership that safeguards national security and fuels the next wave of digital growth.
Why AI-RAN Matters Now
Several converging trends make 2025 pivotal for AI-RAN. Across the Department of War (DOW), the intelligence community, and civil agencies, growing needs for enhanced mobile broadband capabilities and more robust security have driven deployment of an initial set of private 5G networks. As adoption expands, agencies will identify new use cases spurring demands for more agile edge networks.
Executive Order 14320, Promoting the Export of the American AI Technology Stack; mandates within the National Defense Authorization Act around 5G; and national spectrum policy initiatives from the National Telecommunications and Information Administration (NTIA) point to a federal push to secure U.S. telecom technology stacks. These policy moves create a regulatory foundation and strategic imperative to guide AI-native 6G network deployments.
AI-RAN represents a broader shift toward greater ecosystem-driven innovation. Multiple component providers can participate through open application programming interfaces (APIs), enabling network apps and edge AI applications, similar to how mobile app ecosystems transformed consumer technology. In addition, the rapid expansion of the AI-RAN Alliance to more than 100 members signals industry alignment around a common vision for this innovation and change. The coalition includes technology companies and academic institutions all working toward the integration of AI with RAN, with the goal of advancing RAN performance and enabling new capabilities and use cases.
Understanding AI-RAN
Every second, millions of radio transmissions use a spectrum that extends from 600 megahertz to beyond 100 gigahertz. These transmissions can include voice calls, data packets, video streams, sensor readings, GPS coordinates, encrypted military communications, and other media. To manage this profusion of traffic, AI-RAN integrates artificial intelligence directly into the radio access network, which is the infrastructure layer connecting end-user devices from the edge to the broader telecom network.
This integration operates through the deployment of AI models that continuously optimize power control, beamforming, interference mitigation, and anomaly detection, with the ability to continuously train these models based on observed traffic patterns and network conditions. Traditional cell towers function as sophisticated relay stations; AI-RAN changes them into thinking machines.
As mentioned, AI-RAN will transform networks in two fundamental ways. First, the application of AI to wireless networks will drive new levels of spectral and power efficiency and make the network more programmable to adjust to multiple types of scenarios and use cases. This programmability will reduce the need for manual configurations while making the network more adaptable to changes in demand, interference, and outages.
In addition, the open programmability of AI-RAN will enable new network features. For example, industry and government have been developing new integrated sensing and communications (ISAC) capabilities, a key feature that will be incorporated in future 6G standards. With ISAC, the network now becomes a sensing system with the ability to detect objects in its vicinity, unlocking the potential for a plethora of novel applications.
Second, AI-RAN will allow for the same infrastructure that is providing the RAN to also deliver edge AI applications and workloads. Commercially, this critical feature will help telecom providers better monetize their infrastructure investment while offering mission operators at a forward operating base a reduction in the compute footprint needed to provide advanced wireless and AI services.
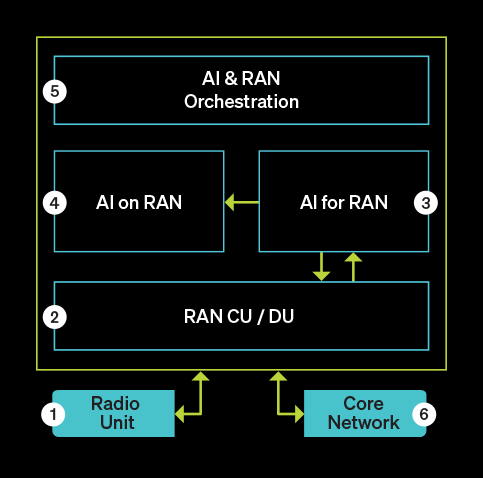
AI-Ran Server: At-a-Glance
- Radio Unit (RU) transmits & receives radio frequency signals from mobile devices
- Ai-native Centralized Unit (CU)/Distributed Unit (DU) uses AI to process and transmit wirelss signal via the RU to & from mobile devices
- AI for RAN Applications dynamically optimize network performance
- AI on RAN Applications enable AI inferencing at the edge
- AI & RAN Orchestration is a software control later that coordinates, manages, and optimizes radio access networks (RAN) using AI and automation
- Core Network is the central backbone connecting the AI-RAN platform to the broader internet and other networks
AI-RAN differs fundamentally from earlier network virtualization approaches. While virtualized RAN (vRAN) architectures made networks more vendor-agnostic, AI-RAN makes them intelligent. It takes the same AI techniques revolutionizing language processing and computer vision and uses them to transform radio wave management. Beyond routing traffic, AI-RAN systems use neural networks that learn from patterns and anticipate congestion, allowing for precise, instant adjustments.
The AI-RAN systems of the future will run on models that understand the deep physics of radio wave propagation and the tactics of electronic warfare, all rolled into a single AI system that can adapt to shifting scenarios. Technical implementation includes network apps that execute AI algorithms in sub-1-millisecond loops. These models range from optimization algorithms to sophisticated neural networks capable of processing computer vision or natural language tasks.
Federal Mission Use Cases
For federal agencies, the time is now to start pilots so that decision makers can evaluate the new technology and influence 6G standards and technology development if needed. Here are potential areas of focus:

Autonomous systems represent one the most compelling federal use cases for AI-RAN because they require split-second coordination among multiple types of sensors during operation in contested network environments. Today’s autonomous vehicles, drones, and unmanned maritime systems operate largely in isolation, making independent decisions based on locally processed sensor data, which limits operational effectiveness.

For autonomous intelligence, surveillance, and reconnaissance (ISR) platforms, AI-RAN enables unmanned aerial and ground vehicles to stream and analyze sensor data locally while adapting communication links to conditions on the ground. Instead of losing capability when traditional links fail, platforms become more resilient as the network intelligently adapts.
Pop-up disaster response networks address critical needs for Federal Emergency Management Agency, Department of Homeland Security, and Coast Guard operations requiring rapidly deployable communication infrastructure in areas without traditional networks. AI-RAN enables portable cell sites as converged infrastructure offering both advanced communications and mission-focused edge applications.

Border security and critical infrastructure monitoring benefit from AI-RAN’s edge inference capabilities on video and thermal sensor feeds. Rather than streaming raw surveillance data to centralized processing centers, network infrastructure identifies anomalies and automatically allocates additional bandwidth to priority alerts.

Other high potential use cases include smart cities and intelligent transportation networks, air traffic control, and energy optimization across large facilities and campuses.
The Road to 6G
Looking ahead, the current evolution to AI-native 6G follows an accelerated cycle that departs from traditional telecom transitions. Software-defined network architectures compress development timelines by reducing hardware dependencies across standards development, testing, and compliance cycles. This enables more rapid iteration than previous hardware-centric generations.
The Urgent Imperative for U.S. Leadership in 5G
Opportunity to shape the next big technology that will enable every sector globally
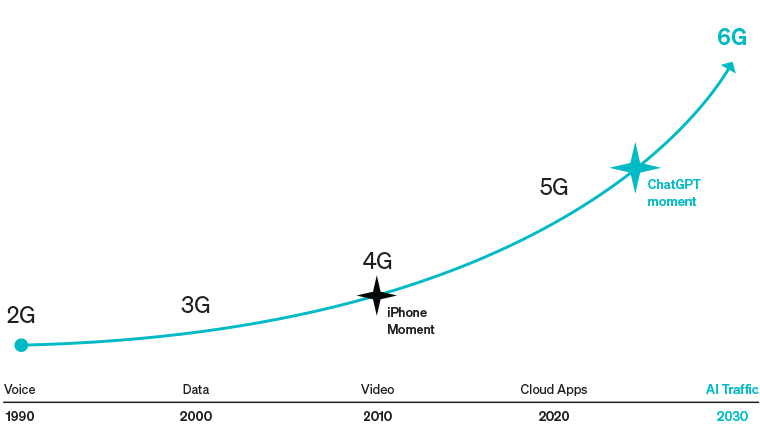
Developed by a consortium of seven leading telecom standard development organizations, 3GPP Release 18-19 (5G-Advanced), finalizing through 2024–2026, is establishing AI/ML service enablers within RAN elements as the technical foundation. Release 20 (2026–2028) features dedicated 6G studies, with Release 21 codifying core specifications for commercial availability around 2030–2031.
Helping drive industry momentum is the NVIDIA-led AI-WIN project. This project, announced in March 2025, brings together Booz Allen and NVIDIA along with T-Mobile, MITRE, Cisco, and ODC to develop an AI-native wireless network stack for 6G on the NVIDIA AI Aerial platform. Our collaboration focuses on creating AI-native hardware, software, and architectures that improve services for potentially billions of users.
To support this effort, Booz Allen is developing AI-RAN algorithms as well as approaches to secure the AI-native 6G wireless platform. Through our NextG lab, a dedicated, secure test environment including a leading-edge carrier-grade network, we will conduct functional, performance integration and security testing to ensure the resilience and security of the platform against the most sophisticated adversaries. We will also lead field trials for advanced use cases such as autonomy and robotics. The AI-WIN approach promises to compress traditional telecom development cycles by embedding AI functionality from the start rather than retrofitting existing architectures, positioning America to lead 6G development.
How to Prepare: Agency Action Plan
Federal agencies can successfully deploy AI-RAN within their environments by following several key principles:
- Establish a cross-functional tiger team. Bring together network engineers, spectrum planners, AI specialists, cybersecurity experts, and acquisition professionals. AI-RAN’s interdisciplinary nature requires this integrated expertise.
- Launch pilot programs immediately. Pilots provide safe environments to discover vulnerabilities and failure modes, streamlining preparation for future deployment.
- Embrace open, modular architectures. Align with existing Open Radio Access Network (O-RAN) frameworks and open APIs to prevent vendor lock-in while enabling rapid AI model updates as algorithms improve.
- Build in security and governance from day one. AI-RAN introduces new attack surfaces through AI models and edge processing. Implement zero trust architectures for RAN elements and establish model risk management procedures.
- Shape policy and spectrum strategy. Ensure that mission-critical frequency bands and spectrum-sharing frameworks allow optimization using AI. Shape NTIA and Federal Communications Commission regulatory environments rather than adapting to them.
- Plan for sustained operations and talent. AI-RAN requires ML operations capabilities, radio frequency engineers who understand AI, and continuous testing ranges for model updates. Build these capabilities in parallel with technical deployments.
- Consider alternative procurement mechanisms. Given AI-RAN’s hybrid nature (integrated hardware, software, and network) and emerging status, tools like other transaction authorities or commercial solutions opening pathways may be more effective for acquiring an initial AI-RAN technology stack.
Act Early, Lead Boldly
AI-RAN represents a fundamental shift toward intelligent, adaptive infrastructure that optimizes itself and hosts mission-critical AI services at the edge. This dual capability makes it central to 6G architecture and essential for future federal operations.
America has a small window to reassert telecom leadership through investment in open, AI-native architectures. Success requires moving beyond traditional procurement toward active participation in standards and technology development, aggressive pilot programs, and policy alignment.
The convergence toward AI-native 6G will continue accelerating with or without U.S. leadership. American agencies and companies can shape this transformation or be forced to adapt to architectures developed elsewhere. With proven deployment experience, strong industry partnerships, and clear mission requirements, federal agencies are positioned to lead this transition with decisive action.
But agencies shouldn’t wait for 6G’s anticipated deployment before acting. Current 5G-Advanced infrastructure provides the foundational compute and edge processing power to implement AI-RAN solutions today. Moving ahead now will enable agencies to gain strategic advantages in network resilience, spectrum efficiency, and operational intelligence while building knowledge to streamline future 6G integration.
The path forward demands immediate steps: select pilot sites, join industry alliances, align spectrum policies, establish governance frameworks, and build talent pipelines necessary to own advanced capabilities. In the race to 6G, intelligence wins. The future will belong to nations that teach their networks to think.







